-This question was submitted by a user and answered by a volunteer of our choice.
Return Outwards
In layman’s language, return outwards refers to the goods returned by the customer to the supplier (or) manufacturer due to various issues found in the goods (say- quality, defects, or damages). Return outwards is also known as purchase returns.
The amount of return outwards (or) purchase returns is deducted from the total purchases of the firm. It is treated as a contra-expense transaction. A Contra expense account is a ledger account where the expenses are deducted from gross revenue or sales.
Return outwards holds the credit balance and is placed on the credit side of the trial balance.
Journal Entry for Return Outwards
As per modern rules,
a) Entry for the purchase of goods
| Particulars | Debit | Credit | Modern rules |
| Purchases A/c | Amt | Increase in expenses | |
| To Supplier’s A/c | Amt | Increase in liability |
This journal entry is passed when the goods are being purchased. The purchases account is debited since it is an increase in expenses. The supplier’s account is credited since this is leading to an increase in liability.
b)Entry on the return of goods purchased
| Particulars | Debit | Credit | Modern rules |
| Supplier’s A/c | Amt | Decrease in liability | |
| To Purchases A/c | Amt | Decrease in Expenses |
This journal entry is passed for purchase returns or return outwards. As there is a returns taking place, it is reducing the expenses hence the purchases account is credited. The supplier’s account is debited since there is decrease in liability as he is returning the goods.
As per traditional rules,
a) Entry for the purchase of goods
| Particulars | Debit | Credit | Rules |
| Purchases A/c | Amt | Debit the expenses, losses | |
| To Supplier’s A/c | Amt | Credit the giver |
As purchases are an expense it is a nominal account, hence it is debited. The supplier’s account is a personal account, hence the account is credited since he is the giver.
b)Entry on the return of goods purchased
| Particulars | Debit | Credit | Rules |
| Supplier’s A/c | Amt | Debit the receiver | |
| To purchases A/c | Amt | Credit the income, gain |
As the purchases are being sent back to the supplier, the supplier account is debited as per the personal account rule. The purchase account is credited since it is being sent back to the supplier.
Example
Mr Alex purchases 10 washing machines for 1,00,000 from Amazon on a credit period of 30 days. On 20th April he returns all the washing machines to Amazon due to the serious defects in all of its models. Pass journal entries for the above transaction in the books of Mr. Alex.
In the books of Mr Alex
a) As per traditional approch
| Date | Particulars | L.F. | Amount | Nature of Account | Accounting Rule |
| 20th April | Amazon A/c Dr | 100,000 | Personal | Debit- The receiver | |
| To Purchases A/c | 100,000 | Nominal | Credit- The income and gain |
(Being goods returned to Amazon due to serious defects)
b) As per modern approch
| Date | Particulars | L.F. | Amount | Nature of Account | Accounting Rule |
| 20th April | Amazon a/c Dr | 100,000 | Liability | Debit- The Decrease in Liability | |
| To Purchase returns a/c | 100,000 | Expense | Credit- The Decrease in Expense |
(Being goods returned to Amazon due to serious defects)
Placement in Trial Balance
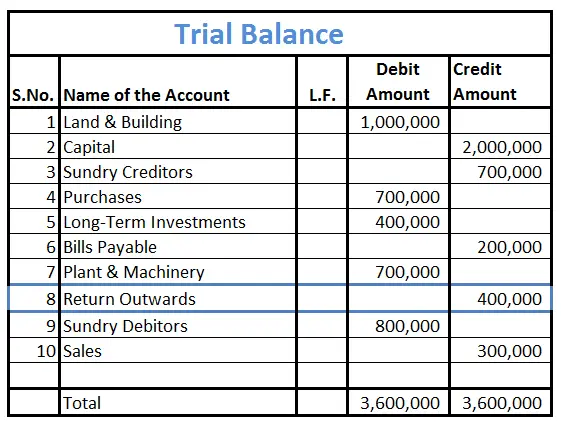
Return outwards appears on the credit side of the trial balance because it will be used to decrease total purchases (contra expense). Secondly, this will reduce inventory leading to a decrease in current assets.
A trading account consists of direct expenses and revenue. As purchases are a direct expense for the company, the purchase returns or returns outwards will be subtracted from the total purchases on the debited side.
Benefits of Returns Outwards subsidiary book
- It helps in keeping track of purchase returns accurately and shows better inventory management.
- This shows the company’s transparency while maintaining the books and their accountability to clear disputes related to returns. This also shows the company’s responsibilty.
