- Meaning and Overview
- Trading Account Format (download PDF/Excel)
- How to Prepare a Trading Account?
- Trading Account vs Profit & Loss Account
- Quiz
Meaning & Overview
A trading account is used to record the sale and purchase of goods/services. This temporary account closes at the end of each accounting period. The purpose of the trading account is to show the gross profit or gross loss made in a particular time period.
The following are some key points to understand about a trading account:
- It is a temporary account that records sales and purchases of goods/services.
- It is used to calculate the gross profit or gross loss on the sale of goods.
- It is closed at the end of every accounting period.
- It is usually combined with the income statement.
- When combined with the profit & loss account, it also helps to determine the net profit/net loss for a period.
In Simple Terms – A trading account keeps track of what a company buys and sells. Every month, the company adds up all the things it bought and sold to determine if it made or lost money. This helps the company know how much money it has from trading activities.

During the period-end closing process of a company, all the financial statements are prepared and finalized. Trading account is the first step in the process of preparing the final accounts of a company.
Related Topic – What is the Journal Entry for Closing Stock?
Type of Account
A trading account is a nominal account in nature.
As per the 3 golden rules of accounting, a trading account is a nominal account. The golden rules of accounting ensure that a business’s financial position and performance are accurately reflected in its financial statements.
With certain accounts such as Trading A/cs, Profit & Loss A/cs, Suspense A/c, etc., it is almost impossible to apply the rules of debit and credit.
As per the modern rules of accounting, the trading account is a type of income statement account that records and reports a business’s trading income & expenses.
Related Topic – Process to Prepare Income Statement from Trial Balance
Trading Account – Format with Example
Activities which generate revenue for the business, such as Sales of Services or Goods, Closing Stock, are shown on the credit side (Right).
In contrast, activities that are part of the cost of goods sold, such as purchasing raw materials, opening stock, direct expenses, etc., are shown on the debit side (Left).
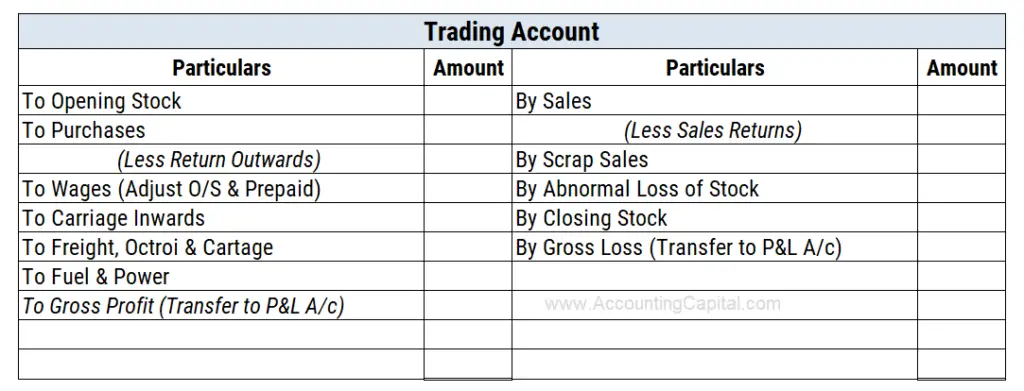
Download Excel Version – Trading Account Sample Format Download Excel Version
Download PDF Version – Trading Account Sample Format Download PDF Version
Related Topic – Difference Between Direct and Indirect Expenses
List of items in a Trading Account
Opening Stock – The unsold stock remaining from the previous accounting period is the opening stock of the current accounting period. Depending on the type of industry, it can include raw materials, unfinished products, and finished goods.
It is typically listed on a company’s trial balance and appears on the debit side of a trading account. A new business’s first year of operation does not include opening inventory.
Purchase and Purchase Returns – Goods and services bought for resale are collectively termed “purchases” for the business. It is a ledger account that records the cost of goods and services that a business purchases on credit. It has a debit balance and includes both cash & credit purchases.
It is important to note that the purchase account does not include the cost of assets purchased for use in the business, such as machinery or furniture.
In the event that the goods are returned for any reason, it is considered a purchase return or a return outwards. Such accounts have a credit balance.
Sales and Sales Return – Goods sold in cash and credit by the business to earn profits are included under the head “Sales”. It has a credit balance and includes both cash and credit sales.
In the event that a customer returns goods for any reason, it is considered a sales return or a return inwards. Such accounts have a debit balance.
Direct Expenses – Expenses incurred while purchasing goods till the time they are brought to a saleable condition are called direct expenses. These are expenses related to the core business operations of a company. For example – Wages, Carriage Inwards, Power, Freight, etc.
Closing Stock – The unsold stock in hand at the end of the current accounting period is placed under the head “closing stock”. It is also known as “inventory” and is shown on the credit side of a trading account.
It is valued at the end of an accounting period at cost or net realisable value, whichever is lower.
Example: If a company records its closing stock at 10,000 but has a market value of 5,000, its financial records will record the lower market value of 5,000. This is because the value of the closing stock must be recorded at its market value, which is the price it could be sold for on the current market.
In this case, the market value is lower than the recorded value, so the lower value must be used in the company’s financial statements.
Gross Profit or Gross Loss – After all items of trading are arranged in the prescribed trading account format. The account must be balanced to determine loss or profit arising from selling activities.
If sales are higher than purchases, i.e. Credit side is bigger than the Debit side, then the difference is termed “Gross Profit“. This is then transferred to the Profit & Loss account.
If purchases are higher than sales, i.e. Debit side is bigger than the Credit side, then the difference is termed “Gross Loss“. This is then transferred to the Profit & Loss account.
Related Topic – Treatment of Closing Stock in Trading A/c
How to Prepare a Trading A/c?
When preparing a trading account, closing entries are typically recorded in a journal proper.
These entries transfer the balances of various temporary accounts, such as revenue and expense accounts, to the appropriate permanent account, such as the owner’s equity account.
By doing this, the temporary accounts are reset to zero and can be used to record transactions in the next period.
To create a trading account in accounting, the following steps can be followed:
Debit Side
- Start with the opening balance of stock and place it as the first item on the debit side.
- Calculate the net purchases of the period (purchases – returns) and record them on the debit side as the next item.
- Next, record all direct expenses, such as wages, carriage, freight, fuel, etc.
Credit Side
- Enter the net sales figures on the credit side (Sales – Returns).
- Record any other direct inflows such as “scrap sales”, etc.
- Closing stock valued at the end of the period is recorded and shown on the credit side of the trading account.
Record the trading account in the company’s financial records and include it with the income statement for the accounting period.
Balancing
The balance of the trading account is calculated by recording the above items on their respective sides, which allows for the determination of gross profit or gross loss.
If the Credit side > the Debit side, it is Gross Profit. It is then transferred to the credit side of a profit & loss account.
If the Debit side > the Credit side, it is Gross Loss. It is then transferred to the debit side of a profit & loss account.
Related Topic – Debit Balance in Trading Account
Purpose of a Trading A/c
The purpose of creating a trading account in accounting is to:
- Maintain a record of goods sold and purchased.
- Establish whether the sale of goods resulted in a gross profit or gross loss.
- Provide a basis for the calculation of net profit or loss.
- Provide information that is useful for management accounting.
- Comply with accounting standards and regulations.
- Prepare the basis of the income statement for the accounting period.
Overall, the main purpose of a trading account is to provide a clear and accurate record of the sales and purchases of goods and to calculate the gross profit or loss on these transactions.
This information is used in the preparation of the income statement and is also used by management to make decisions about the business.
Creating a trading account is an important part of the accounting process and helps to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the company’s financial records.
Related Topic – Credit Balance in Trading Account
Trading Account Vs Profit and Loss A/c
| Basis | Trading A/c | Profit & Loss A/c |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is a statement that records buying & selling (trading) activities of a business. | It is a statement that records all gains and losses incurred by a business. |
| Purpose | A trading account is prepared to calculate gross profit or gross loss. | A profit & loss account is prepared to calculate net profit or net loss. |
| Relation | It is part of the profit & loss account itself. | It is the main account. |
| Items | It consists of direct expenses and gains. | It consists of indirect expenses and gains. |
| Balance | Balance of this account is transferred to the Profit & Loss account. | Balance of this account is transferred to the balance sheet. |
| Example of items | Some examples include – Purchases, Sales, Opening and Closing Stock, Direct Expenses, etc. | Some examples include – Salaries, Rent, Depreciation, Bank Charges, etc. |
Related Topic – How to Prepare Balace Sheet from Trial Balance?
Points to Remember
- Carriage inwards is debited to the trading account, whereas Carriage outwards is debited to the profit & loss account.
- Gross profit can be shown with the help of an equation as well,
- GP = Net Sales – COGS
- COGS = Opening Stock + Net Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
- Net Purchases = Total Purchases – Purchase Returns
- Return inwards are deducted from “Sales” whereas Return outwards is deducted from “Purchases”.
- Trading is a part of the overall profit & loss account (income statement).
Related Topic – Where are Trading Expenses in Final Accounts?
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
>Read Journal Entry for Bad Debts

