Overview of Expenses
The costs paid by a business in order to generate revenue are called expenses. In other words, it is an outflow of funds in exchange for the acquisition of a product or service. For example, rent payments, interest payments, electricity bills, administration expenses, selling expenses, etc.
There are different types of expenses based on their nature and the term of benefit received.
- Direct & Indirect Expenses – All expenses related to the direct cost of goods and services produced are called direct expenses. Whereas, expenses that do not form part of direct costs are called indirect expenses.
- Capital Expense – Expenses incurred for acquiring capital assets, like building, machinery, etc., are called capital expenses.
- Revenue Expense – expenses incurred for day-to-day business operations are revenue expenses.
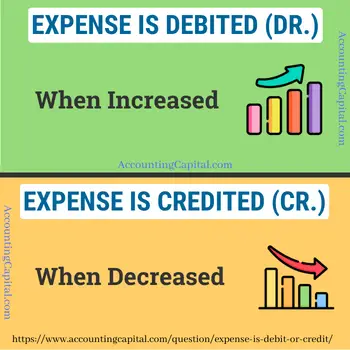
In accounting terms, expenses tend to increase productivity while decreasing owner’s equity. Thus, an increase in expenses should be debited in the books of accounts.
Related Topic – Capitalized Expenditure
As per the Modern Rules of Accounting
| Account | Increase | Decrease |
|---|---|---|
| Expense | Debit (Dr.) | Credit (Cr.) |
Expense is Debited (Dr.) when increased & Credited (Cr.) when decreased.
Why is it like this?
This is a rule of accounting that cannot be broken under any circumstances.
How is it done?
Suppose, you rent a local shop that sells apples & you make a yearly payment towards the shop’s rent (in cash). As a result, this expense would be added to the income statement for the current accounting year because due to this payment the total expenses of your business have increased.
Below is the timeline of how it would be recorded in the financial books.
Step 1 – While making the payment the below journal entry is recorded in the books of accounts. (Rule Applied – Dr. the increase in expense)
| Rent Expense A/c | Debit |
| To Cash A/c | Credit |
(Payment in cash for shop’s rent)
Step 2 – At the time when the expense is transferred to “Profit & Loss A/c”.
| Profit & Loss A/C | Debit |
| To Rent Expense A/C | Credit |
(Shop’s rent expense is transferred to the income statement)
Related Topic – Liability is Debited or Credited?
As per the Golden Rules of Accounting
| Account | Rule for Debit | Rule for Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal | All Expenses and Losses | All Incomes & Gains |
Expense is Debited (Dr.)
As per the golden rules of accounting for (nominal accounts) expenses and losses are to be debited.
A nominal account represents any accounting event that involves expenses, losses, revenues, or gains. It is what you would call a profit and loss or an income statement account. As opposed to personal and real accounts, nominal accounts always start out with a zero balance at the beginning of a new accounting year.
Example
Suppose, you rent a local shop that sells apples & you make a monthly payment towards the shop’s electricity bill (by the bank). Consequently, this payment would be reflected on the income statement.
Below is the timeline of how it would be recorded in the financial books.
Step 1 – In the below example of a journal entry for electricity bill payments “Electricity Charges A/c” is debited. (Rule Applied – Dr. all expenses & losses)
| Electricity Charges A/c | Debit |
| To Bank A/c | Credit |
(Payment by the bank for the shop’s electricity bill)
Step 2 – At the time when the expense is transferred to “Profit & Loss A/c”.
| Profit & Loss A/C | Debit |
| To Electricity Charges A/C | Credit |
(Shop’s rent expense is transferred to the income statement)
If the expense is prepaid, it is an asset to the business and is shown on the asset side of the balance sheet.
Related Topic – Is Income Debit or Credit?
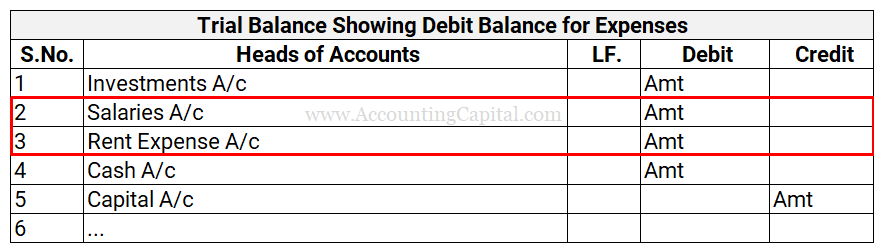
Expenses Inside Trial Balance
Expenses show a debit balance in the trial balance. A trial balance example showing a debit balance for salaries and rent expenses is provided below.
>Read Contra Accounts

