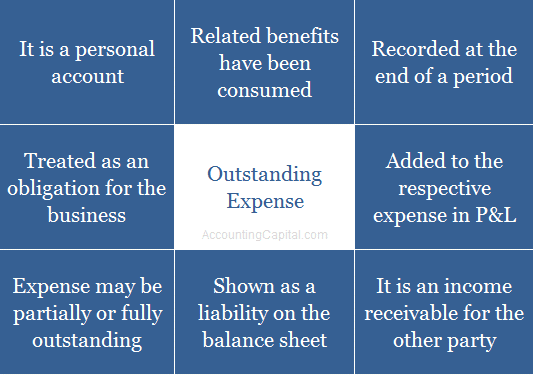
- Meaning and Overview
- Examples
- Outstanding Expenses Journal Entry
- Outstanding Expenses are Asset or Liability?
- Where do Outstanding Expenses Appear?
- Outstanding Expenses in Trial Balance?
- Outstanding Expense is Which Type of Account?
- Treatment in Final Accounts
- Revision Video
- Conclusion
Meaning and Overview
Outstanding expenses are those expenses which have been incurred during the current accounting period and are due to be paid, however, the payment is not made. Such an item is to be treated as payable by the business.
Examples – Outstanding salary, outstanding rent, outstanding subscription, outstanding wages, etc. Outstanding expenses are recorded in books of finance at the end of an accounting period to show the true numbers of a business. They are also casually known as expenses due but not paid, unpaid expenses, arrears, overdue expenses, etc.

Expenses are the amounts paid for goods or services purchased. The accrual concept of accounting records transactions in the books of accounts when they occur regardless of when the money is received or paid.
It is not always possible to make and receive payments immediately, they may be late or in advance. Outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses, accrued income & income received in advance are all a result of held-up payments and receipts.
Related Topic – Expense is Debit or Credit?
Examples
Company-A has a rent obligation of 10,000/month that is due every 10th of the month. On Dec 10th, the company failed to make this payment.
The amount not paid by Company-A on 10th Dec is termed as “Outstanding Rent” in the current year (a classic example of an outstanding expense).
At the end of the period, this “expense due but not paid” impacts the financials of the business. As per accrual accounting, it is supposed to be journalized.
Related Topic – Is Depreciation an Operating Expense?
Outstanding Expenses Journal Entry
In the event that a business fails to make a payment when it is due it becomes an outstanding expense and is treated as a liability.
Journal Entry for Outstanding Expense
| Expense A/c | Debit | Debit the increase in expense |
| To Outstanding Expense A/c | Credit | Credit the increase in liability |
(Being expense not paid on the due date)
Related Topic – What is Adjusted Trial Balance?
Journal Entry for Outstanding Rent
Rent is a periodic payment made to cover the cost of occupying and using a property (land, building, etc.). The payments are made to the owner of the property. It is often paid monthly, or yearly.
In the context of outstanding rent, it refers to rent due for a period that has already passed.
Outstanding rent journal entry should be recorded as follows:
At the time when rent is due and not paid.
| Rent Expense A/c | Debit | Debit the increase in expense |
| To Outstanding Rent A/c | Credit | Credit the increase in rent liability |
(Being unpaid rent recorded)
Journal Entry for Outstanding Salary
Paying employees a salary is a way for employers to compensate them for their work. Most of the time, it is paid monthly and includes some benefits.
It is called an outstanding salary when a payment is due to be made to an employee but he or she has already worked for that period.
Outstanding salary journal entry should be recorded as follows:
At the time when salary is due but not paid.
| Salaries A/c | Debit | Debit the increase in expense |
| To Outstanding Salaries A/c | Credit | Credit the increase in salaries liability |
(Being unpaid salaries recorded)
Journal Entry for Outstanding Wages
There is a slight difference between wages and salaries. It is common practice to refer to part-time jobs, jobs with variable hours, and jobs with repetitive duties as wages instead of salaries.
Usually, wages are paid weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly. The most common difference between salary and wages is that salaries are fixed amounts, but wages are determined by the number of hours an employee works.
Outstanding wages journal entry should be recorded as follows:
At the time when wages are due but not paid.
| Wages A/c | Debit | Debit the increase in expense |
| To Outstanding Wages A/c | Credit | Credit the increase in wages liability |
(Being unpaid wages recorded)
Journal Entry for Outstanding Commission
Commissions are designed to provide incentives and rewards to salespeople for promoting certain products, sales behaviour, or for simply increasing the sold quantities.
A commission payable in the current year that remains unpaid till the end of the year is an outstanding commission.
Outstanding commission payable journal entry should be recorded as follows:
At the time when a commission is owed but not paid.
| Commission A/c | Debit | Debit the increase in expense |
| To Outstanding Commission A/c | Credit | Credit the increase in liability |
(Being unpaid commission recorded)
Related Topic – Journal Entry for Commission Received
Outstanding Expenses are Assets or Liability?
The term “liabilities” refers to money owed by companies or individuals. Money, goods, or services may be used in exchange to pay off liabilities over time. An expense that is unpaid after it is due is considered outstanding and it is treated as a liability (current) for the business.
Reason – The logic of why payment due for an expense is treated as a liability by the business is because the benefit in exchange for the payment is already received. It stays a liability till the time the actual expense owed is paid. It is the obligation and responsibility of the business to pay them off.
Such an expense has an expired value which means the benefit in exchange for the payment is expired.
Why is it considered a current liability?
Liabilities that are generally expected to be settled within the current accounting year (usually 12 months) are called current liabilities.
The expectation around an outstanding expense is to convert it from being a liability to realising it as an expense within a year.
It is typical for current liabilities to be settled with current assets such as cash. In this way, they contribute to the calculation of the current ratio and cash ratio.
Related Topic – Why is Income Received in Advance Treated as Current Liability?
Where do Outstanding Expenses Appear?
Outstanding expenses in balance sheet are viewed as a liability and shown on the balance sheet under the head “Current Liabilities”. Such entries help provide accurate accounting information to both internal and external users of accounting information as well as compliance with accounting laws.
It is shown as a current liability until it is fully paid, after which it is removed from the balance sheet and no longer shown.
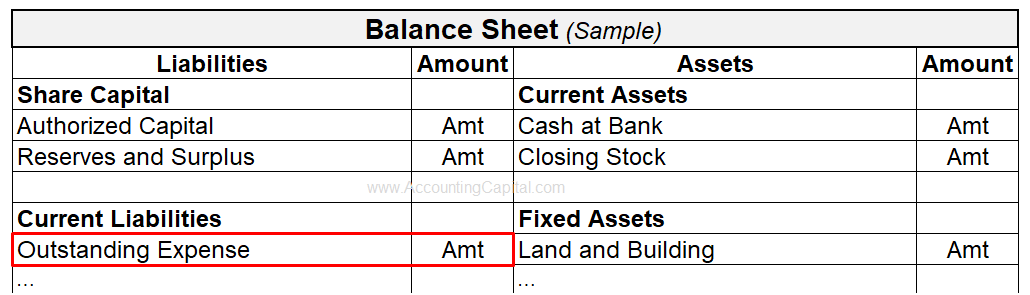
- Expense not paid is an obligation for the business that shows up on the balance sheet to ensure liabilities are not understated.
- It is shown as a current liability because the assumption is that the delayed payment will be settled within one accounting year.
Outstanding Expenses in Trial Balance
If outstanding expenses appear inside the trial balance
In such a scenario it implies that the adjusting entry has already been posted. In this case, it is only shown in the balance sheet as a “current liability” and no adjustment is required in the income statement.
For example, if outstanding wages are shown in the trial balance, they will be recorded on the liabilities section of the Balance Sheet (only). Accounts that appear in the trial balance are only shown in one place in the final accounts/financial statements.
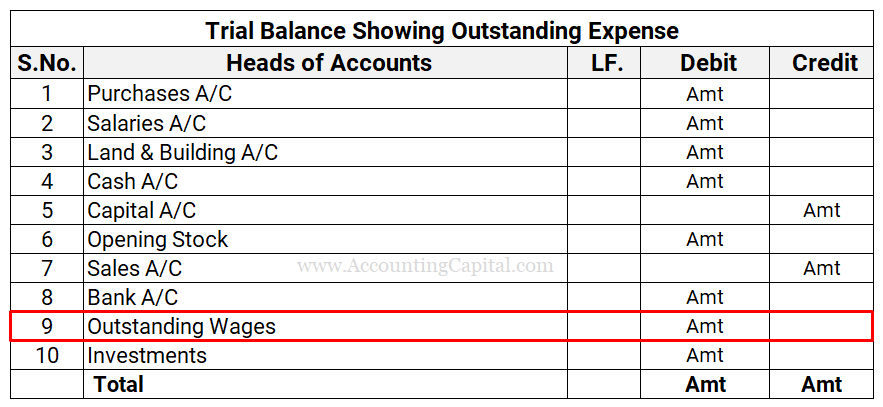
If outstanding expenses appear outside the trial balance
In case it appears outside the trial balance then it is considered an adjustment in the final accounts and adjusted both in the income statement and the balance sheet. (two adjustments)
Trading & Income Statement – Show as an addition to respective indirect expense
Balance Sheet – Show under “Current Liabilities” on the balance sheet
Related Topic – List of Debit and Credit Items in Trial Balance
Outstanding Expenses is Which Type of Account?
The outstanding expense is a personal account and is treated as a liability for the business. It is also shown on the liability side of a balance sheet.
Due to its indirect link to a person or group, it makes sense to call it a representative personal account. As per the rules of debit and credit, it follows the rule of Dr. the receiver and Cr. the giver.
However, as per modern accounting rules, it is a liability and follows the rule of Cr. the increase and Dr. the decrease.
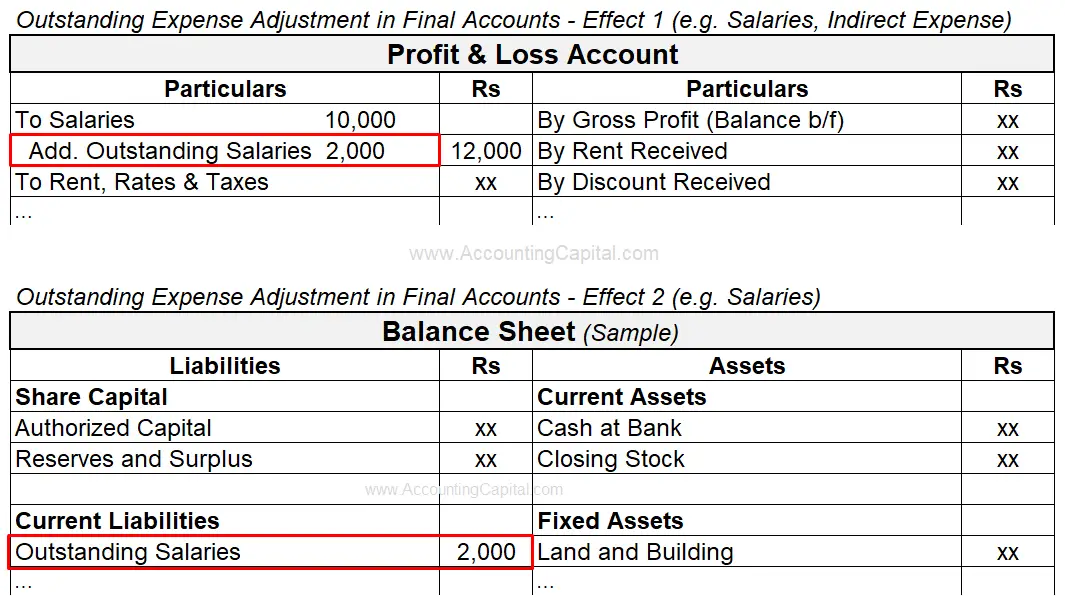
Treatment in Final Accounts
Treatment of Outstanding Expenses in Financial Statements/Final Accounts
- Trading & Profit and Loss A/c Show on the Dr. side (add to respective direct or indirect expense)
- Balance Sheet: Show on the “Liabilities” side (under the head “Current Liabilities”)
Example
In the year, a company paid Rs 10,000 in salaries and estimated the outstanding salaries to be Rs 2,000. Adjust outstanding expenses in final accounts at the end of the period.
Revision and Highlights
Highly Recommended!!
Do not miss our 1-minute revision video and the quiz below. This will help you quickly revise and memorize the topic forever. Try them :)
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
Conclusion
A similar concept is accrued expense, which can be used interchangeably but it differs slightly from outstanding expense. Both of them differ in the following ways:
Business expenses that have been incurred but are not due to be paid yet are known as accrued expenses. No matter when the payment is made, this type of expense is recorded in the books of accounts when it is incurred.
However, the term outstanding expense refers to an expense that has been incurred and is already past due.
It is uncommon to see frequent overdue payments as it impacts a buyer’s ability to purchase raw materials on credit and any delayed payment is seen as a doubtful debt which is different from bad debts.
What may happen if outstanding expenses are not recorded?
- There will be an understatement of liabilities.
- There will be an overstatement of profits.
- As a result, there is a risk that the financial statements will be incorrect.
- The company may have to face legal issues as a consequence of this.
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 34 – Outstanding Expenses
>Read Bad Debts

