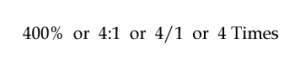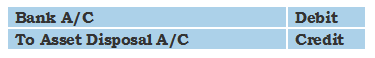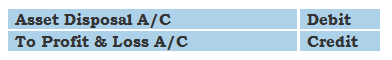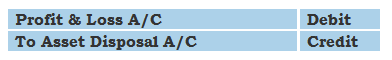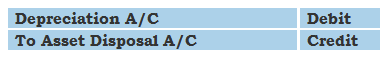Accounting Ratios – Definition
Accounting ratios are mathematical expressions demonstrating a relationship between two independent or related accounting figures. Such ratios are calculated on the basis of accounting information. It is usually expressed as A:B, A to B, A/B, etc.
With the help of accounting ratios, a comparative study becomes possible, for example, if you have to prepare a 300-page book and you have a time limit of 100 days to do it, you can now analyze and evaluate (300/100 = 3/1 or 3:1) that you for every 3 pages you have 1 day.
Ratios can be expressed in any of the below formats;
Four Ways to Show Accounting Ratios
- Percentage – This type of display is shown in the form of a percentage.
For example,
Current Ratio = Current Assets/Current Liabilities
Lets say, Current assets = 4,00,000 & Current liabilities = 1,00,000
Current Ratio = 4,00,000/1,00,000 = 4/1 or if seen in percentage form it is (4,00,000/1,00,000)*100 = 400%
The above example shows that at the time of calculation current assets were 400% of current liabilities.
- Pure – Accounting ratios can be presented in quotient form.
For example,
Acid Test Ratio = Liquid Assets/Current Liabilities
Lets say, Liquid assets = 4,00,000 & Current liabilities = 1,00,000
Acid Test Ratio = 4,00,000/1,00,000 = 4 or it can also be shown as 4:1
- Fraction – This involves expressing a ratio in the form of a fraction or proportion.
For example,
Operating Cash Flow Ratio = Cash flow from operations/Current Liabilities
Lets say, Cash flow from operations = 3,00,000 & Current liabilities = 2,00,000
Operating cash flow ratio = 3,00,000/2,00,000 = 3/2, this is the ratio in fraction form and it means for every 3 units of current assets the company has 2 units of current liabilities to be paid.
- Times or Turnover Rate – Accounting ratios are also depicted in the form of ‘number of times” or “turnover rate” in comparison to another item.
For example,
Debt to Asset Ratio = Total Debt/Total Assets
Lets say, Total Debt = 3,00,000 & Total Assets = 1,00,000
Debt to Asset Ratio = 3,00,000/1,00,000 = 3 Times
It shows the relationship between Total debt and Total assets which in this case is 3 times. So, Total debt of the company is 3 times its total assets.
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
>Read Ratio Analysis